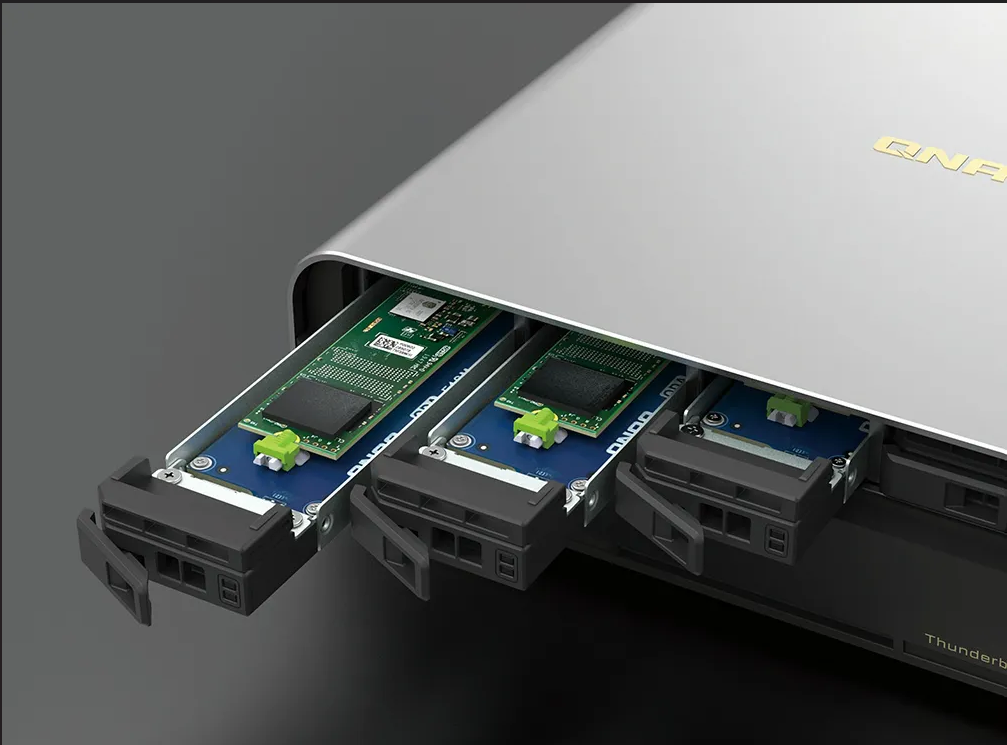
All Flash Storage
All Flash Storage
All-flash storage refers to a type of data storage system that uses solid-state drives (SSDs) exclusively for data storage, as opposed to traditional storage systems that rely on hard disk drives (HDDs). SSDs are much faster and more reliable than HDDs because they store data in NAND flash memory chips, which have no moving parts and can access data nearly instantly. Here are some key features and benefits of all-flash storage:
Speed: All-flash storage provides significantly faster data access and transfer speeds compared to HDDs. This is critical for applications and workloads that require low latency and high throughput, such as database operations, virtualization, and high-performance computing.
Reliability: SSDs are more reliable than HDDs because they are less prone to mechanical failures, such as disk platter crashes. This increased reliability leads to higher data availability and reduced downtime.
Energy Efficiency: All-flash storage systems are typically more energy-efficient than traditional storage systems because they consume less power and generate less heat. This can result in cost savings on both power and cooling.
Space Efficiency: SSDs are smaller and more compact than HDDs, allowing for more storage capacity in a smaller physical footprint. This is especially advantageous in data centers where space is at a premium.
Scalability: All-flash storage systems are highly scalable, allowing organizations to easily add more storage capacity as needed to accommodate growing data requirements. Many storage vendors offer scale-out architectures for seamless expansion.
Reduced Management Complexity: Flash storage systems often come with advanced management and data optimization features, such as data deduplication, compression, and thin provisioning, which can help streamline storage administration and reduce the total cost of ownership.